
Port Types and Speeds Compared
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is one of the most widely used technologies in modern electronics. From charging smartphones to transferring files between computers, USB has evolved through multiple generations of standards and connector types. With so many versions and shapes, it can be tricky to know what’s what. This guide will help you make sense of the differences.
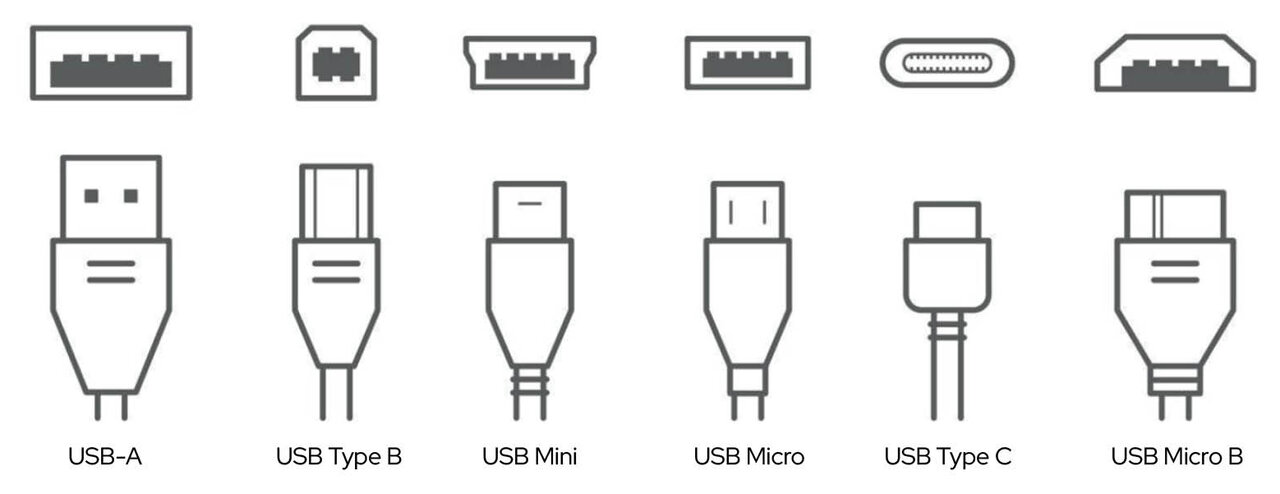
Connector Types Explained
USB ports come in several shapes; each designed for different devices and purposes:
USB‑A The classic rectangular connector found on desktop PCs, older laptops, TVs, game consoles, and media players.
USB‑B / Mini‑B Squarish connectors, often used for printers, scanners, and some external hard drives. Mini‑B was common in digital cameras and smaller devices.
Micro‑B Slim connectors widely used on Android™ smartphones, portable hard drives, and other compact electronics.
USB‑C The modern industry standard. Small, oval, and reversible, USB‑C is now used across smartphones, tablets, laptops, and accessories. It supports faster charging, higher data speeds, and even video output through “alternate modes” such as HDMI, VGA, and DisplayPort.
USB Specifications at a Glance
Specification | Previously knowns as | Connector Types | Bandwidth / Max Data Transfer Speed | Brand Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
USB 2.0 | USB-A USB-B USB MicroB USB Mini B USB-C | 480 Mbit/s (60MB/s) | High Speed, also Hi-Speed | |
USB 3.2 Gen 1 | USB 3.1 Gen 1 USB 3.0 | USB-A USB-B USB MicroB USB-C | 5 Gbit/s (625 MB/s) | SuperSpeed 5Gbps |
USB 3.2 Gen 2 | USB 3.1 or USB 3.1 Gen 2 Superspeed 10Gbps | USB-A USB-B USB MicroB USB-C | 10 Gbit/s (1.25 GB/s) | SuperSpeed 10Gbps |
USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 | USB-C | 20 Gbits/s (2.5 GB/s) | SuperSpeed 20Gbps | |
USB4 Gen 2x2 | USB-C | 20 Gbits/s (2.5 GB/s) | USB4 20 Gbps | |
USB4 Gen 3x2 | USB-C | 40 Gbits/s (5 GB/s) | USB4 40 Gbps |

Why Speeds Matter
The speed of your USB connection determines how quickly data can move between devices. USB 2.0, with its 480 Mbit/s limit, is fine for keyboards, mice, and basic file transfers. USB 3.2, offering 5–10 Gbit/s, is far better suited for external hard drives, HD video, and faster backups. At the high end, USB4 delivers up to 40 Gbit/s, making it ideal for professional applications such as 4K/8K video editing, VR headsets, and large‑scale data transfers. Choosing the right standard ensures you get the performance your devices are capable of.
Power Delivery and Charging
Beyond data transfer, USB has become a universal charging solution. USB‑C with Power Delivery (PD) can deliver up to 240W, making it powerful enough to charge laptops, monitors, and desktop PCs. Faster charging depends not only on the connector but also on the cable and device support. This versatility is one reason USB‑C has become the preferred connector across industries.

Important Point to Remember
Not all USB‑C cables are created equal, so it’s important to check their ratings for both data transfer and charging. Matching the right cable with the right port ensures you’ll enjoy the fastest speeds and most reliable performance.